
Lumbar Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) For Lower Back Pain
You may feel pain if a lumbar facet joint is injured. Sometimes it feels like muscle tension. Other times it can be severe pain. The cartilage inside the joint may be injured. Other times only connecting ligaments surrounding the joint are injured. Facet pain also depends on which joint is affected. Lumbar facet joint pain can occur in an area from your low back down to your buttocks, groin, and hips. The diagram, above right, shows areas of pain usually associated with lumbar facet injuries.
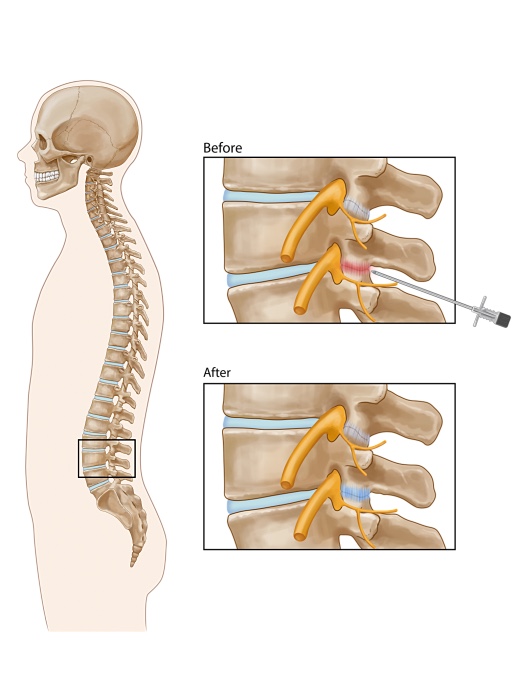
Facet joints connect the vertebrae, the bones of the spine. They help guide your spine when you move. The low back area of the spine is called the lumbar region. It contains five vertebrae. Facet joints are found on both sides of the spine. Each is about the size of a thumbnail. Lumbar facet joints are named for the vertebrae they connect and the side of the spine where they are found. The left L4-5 facet joint, for example, joins the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae on the left side. Medial branch nerves are found near facet joints. They communicate pain from the facet joint. They tell the brain when facet joints have been injured.
A LUMBAR RADIOFREQUECY ABLATION (RFA) is an outpatient procedure for treating lower back, buttock, hip, and groin pain. It is also called lumbar facet thermal coagulation or rhizotomy. This information has been provided by your doctor so you can better understand this procedure. Your doctor will make the best recommendation for your specific needs.
WHAT ARE LUMBAR FACET JOINTS?
Facet joints connect the vertebrae, the bones of the spine. They help guide your spine when you move. The low back area of the spine is called the lumbar region. It contains five vertebrae. Facet joints are found on both sides of the spine. Each is about the size of a thumbnail. Lumbar facet joints are named for the vertebrae they connect and the side of the spine where they are found. The left L4-5 facet joint, for example, joins the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae on the left side. Medial branch nerves are found near facet joints. They communicate pain from the facet joint. They tell the brain when facet joints have been injured.
WHAT IS LUMBAR FACET JOINT PAIN?
You may feel pain if a lumbar facet joint is injured. Sometimes it feels like muscle tension. Other times it can be severe pain. The cartilage inside the joint may be injured. Other times only connecting ligaments surrounding the joint are injured. Facet pain also depends on which joint is affected. Lumbar facet joint pain can occur in an area from your low back down to your buttocks, groin, and hips. The diagram, above right, shows areas of pain usually associated with lumbar facet injuries.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE LUMBAR FACET PAIN?
If you have pain in one or more of these areas, and it has lasted longer than two months, you may have lumbar facet pain. Common tests such as x-rays or MRls may not always show if a facet joint is causing pain. The best way to
diagnose facet pain is to block the pain signal in a medial branch nerve with a local anesthetic (numbing medicine).
WHAT IS A LUMBAR RFA?
RFA uses radiofrequency energy to disrupt nerve function. When this is done to a lumbar medial branch nerve, the nerve can no longer transmit pain from an injured facet joint.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING AN RFA?
A local anesthetic will be used to numb your skin. The doctor will then insert a small needle near the facet joint. Fluoroscopy, a type of x-ray, will be used to position the needle. The doctor will then check to make sure it is at the correct nerve by stimulating it. This may cause muscle twitching and provoke some of your pain. Once the needle is properly placed, the nerve will be numbed. Radiofrequency energy will then be used to disrupt the medial branch nerve. This is often repeated at more than one level of the spine.
WHAT HAPPENS AFTER AN RFA?
You will be monitored for up to 30 minutes after the RFA. When you are ready to leave, the staff will give you discharge instructions. You will also be given a pain diary. It is important to fill this out because it helps your doctor know how the RFA is working. Take it easy for the rest of the day. You may feel sore for one to four days. It may be due to muscle and nerve irritation. Your back may feel numb, weak, or itchy for a couple weeks. Maximum pain relief normally comes within 2-3 weeks.
HOW LONG CAN I EXPECT PAIN RELIEF?
While it varies from patient to patient, nerves can take up to 18 months to regenerate after an RFA. Your pain may or may not return when the nerves regenerate. If it does, another RFA can be done.
Cervical Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) for Neck Pain and Headaches
A CERVICAL RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION (RFA) is an outpatient procedure for treating headaches, neck, shoulder, and upper back pain. It is also called cervical facet thermal coagulation or rhizotomy. This information has been provided by your doctor so you can better understand this procedure. Your doctor will make the best recommendation for your specific needs.
WHAT ARE CERVICAL FACET JOINTS?
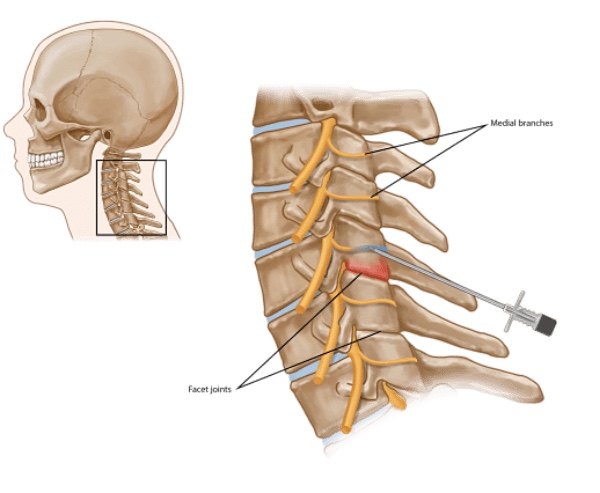
Facet joints are found on both sides of the spine. Each is about the size of a thumbnail. Cervical facet joints are named for the vertebrae they connect and the side of the spine where they are found. The left C2-3 facet joint, for example, joins the 2nd and 3rd vertebrae on the left side. Facet joints not only connect the vertebrae, they also guide Facet Cartilage the spine during movement.
WHAT IS CERVICAL FACET JOINT PAIN?
Cervical facet joint pain is a result of injury, either to the cartilage inside the joint or the connecting ligaments surrounding the joint. Pain from an injured cervical facet joint may range from muscle tension to more severe pain. Depending on which joint is affected, the pain may occur in an area from your head down to your shoulder blade.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE CERVICAL FACET PAIN?
If you have pain in one or more of these areas, and it has lasted longer than two months, you may have cervical facet pain. Common tests such as x-rays or MRls may not always show if a facet joint is the reason for your pain. The best way to diagnose facet pain is to block the pain signal with a cervical medical branch block.
WHAT IS A CERVICAL RFA?
An RFA uses radiofrequency energy to disrupt nerve function. When this is done to a cervical medial branch nerve, the nerve can no longer transmit pain signals from an injured facet joint.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING AN RFA?
A local anesthetic will be used to numb your skin. The doctor will then insert a small needle near the facet joint. Fluoroscopy, a type of x-ray, will be used to position the needle. The doctor will then check to make sure it is at the correct nerve by stimulating it. This may cause muscle twitching and provoke some of your pain. Once the needle is properly placed, the nerve will be numbed. Radiofrequency energy will then be used to disrupt the medial branch nerve. This is often repeated at more than one level of the spine.
WHAT HAPPENS AFTER AN RFA?
You will be monitored for up to 30 minutes after the injection. Before you leave, you will be given discharge instructions. You may feel sore for one to four days. This is normal, and may be caused by muscle and nerve irritation. Your neck or upper back may feel numb, weak, or itchy for a couple of weeks. Be patient, as full pain relief normally takes 2-3 weeks.
HOW LONG CAN I EXPECT PAIN RELIEF?
While it varies from patient to patient, nerves can take up to 18 months to regenerate after an RFA. Your pain may or may not return when the nerves regenerate. If it does, another RFA can be done.
